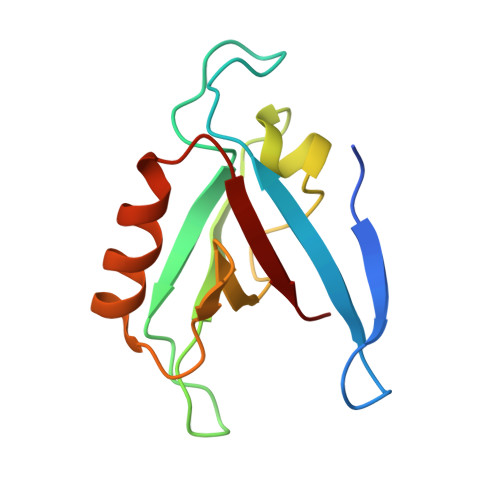
Solution Structure of the RIM1alpha PDZ Domain in Complex with an ELKS1b C-terminal Peptide
Lu, J., Li, H., Wang, Y., Sudhof, T.C., Rizo, J.(2005) J Mol Biol 352: 455-466
- PubMed: 16095618
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.07.047
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ZUB - PubMed Abstract:
PDZ domains are widespread protein modules that commonly recognize C-terminal sequences of target proteins and help to organize macromolecular signaling complexes. These sequences usually bind in an extended conformation to relatively shallow grooves formed between a beta-strand and an alpha-helix in the corresponding PDZ domains. Because of this binding mode, many PDZ domains recognize primarily the C-terminal and the antepenultimate side-chains of the target protein, which commonly conform to motifs that have been categorized into different classes. However, an increasing number of PDZ domains have been found to exhibit unusual specificities. These include the PDZ domain of RIMs, which are large multidomain proteins that regulate neurotransmitter release and help to organize presynaptic active zones. The RIM PDZ domain binds to the C-terminal sequence of ELKS with a unique specificity that involves each of the four ELKS C-terminal residues. To elucidate the structural basis for this specificity, we have determined the 3D structure in solution of an RIM/ELKS C-terminal peptide complex using NMR spectroscopy. The structure shows that the RIM PDZ domain contains an unusually deep and narrow peptide-binding groove with an exquisite shape complementarity to the four ELKS C-terminal residues in their bound conformation. This groove is formed, in part, by a set of side-chains that is conserved selectively in RIM PDZ domains and that hence determines, at least in part, their unique specificity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, 5323 Harry Hines Blvd., Dallas, TX 75390, USA.