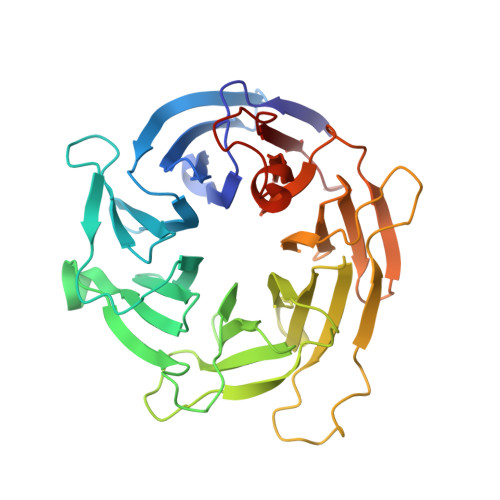
The 1.1-a structure of the spindle checkpoint protein bub3p reveals functional regions.
Wilson, D.K., Cerna, D., Chew, E.(2005) J Biol Chem 280: 13944-13951
- PubMed: 15644329
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M412919200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YFQ - PubMed Abstract:
Bub3p is a protein that mediates the spindle checkpoint, a signaling pathway that ensures correct chromosome segregation in organisms ranging from yeast to mammals. It is known to function by co-localizing at least two other proteins, Mad3p and the protein kinase Bub1p, to the kinetochore of chromosomes that are not properly attached to mitotic spindles, ultimately resulting in cell cycle arrest. Prior sequence analysis suggested that Bub3p was composed of three or four WD repeats (also known as WD40 and beta-transducin repeats), short sequence motifs appearing in clusters of 4-16 found in many hundreds of eukaryotic proteins that fold into four-stranded blade-like sheets. We have determined the crystal structure of Bub3p from Saccharomyces cerevisiae at 1.1 angstrom and a crystallographic R-factor of 15.3%, revealing seven authentic repeats. In light of this, it appears that many of these repeats therefore remain hidden in sequences of other proteins. Analysis of random and site-directed mutants identifies the surface of Bub3p involved in checkpoint function through binding of Bub1p and Mad3p. Sequence alignments indicate that these surfaces are mostly conserved across Bub3 proteins from diverse species. A structural comparison with other proteins containing WD repeats suggests that these folds may bind partner proteins using similar surface areas on the top and sides of the propeller. The sequences composing these regions are the most divergent within the repeat across all WD repeat proteins and could potentially be modulated to provide specificity in partner protein binding without perturbation of the core structure.
Organizational Affiliation:
Section of Molecular and Cellular Biology, University of California, Davis, California 95616, USA. dave@alanine.ucdavis.edu