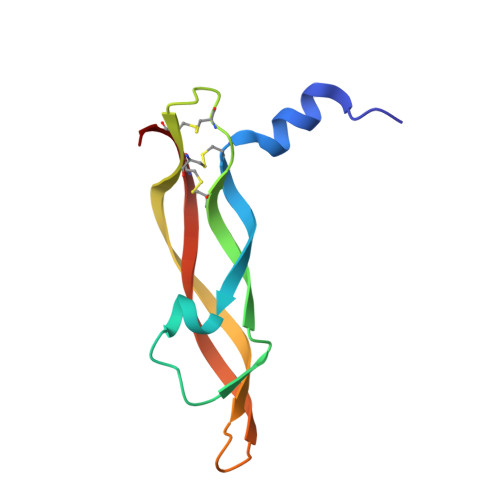
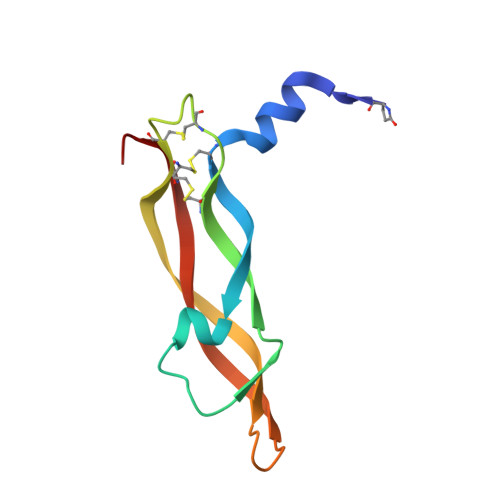
Crystal structures of novel vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) from snake venoms: insight into selective VEGF binding to kinase insert domain-containing receptor but not to fms-like tyrosine kinase-1.
Suto, K., Yamazaki, Y., Morita, T., Mizuno, H.(2005) J Biol Chem 280: 2126-2131
- PubMed: 15542594
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M411395200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WQ8, 1WQ9 - PubMed Abstract:
Vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A(165)) exerts multiple effects upon binding to the fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (Flt-1) and the kinase insert domain-containing receptor (KDR). We recently identified two novel snake venom VEGFs (vammin and VR-1) having unique properties. These VEGFs, designated VEGF-Fs, are highly specific ligands for the kinase insert domain-containing receptor and exhibit potent biological activity both in vitro and in vivo when compared with VEGF-A(165). Here, we solved the crystal structures of vammin and VR-1 at 1.9 and 2.0 A resolutions, respectively. Both structures are very similar to each other, and these structures exhibit similar but significantly different features from the known structures of other VEGFs. These differences include a conformational difference in receptor-binding loop 3 caused by an amino acid residue insertion and a difference in surface potential on the possible binding surface for domain 3 of the receptor. These structural differences may be related to the highly selective ligand properties of VEGF-F.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, 2-1-2, Kannondai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8602, Japan.