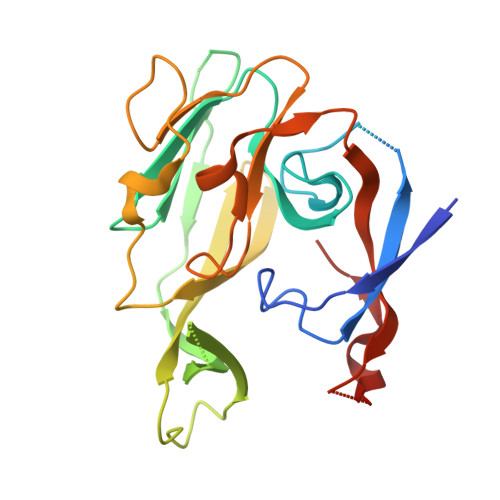
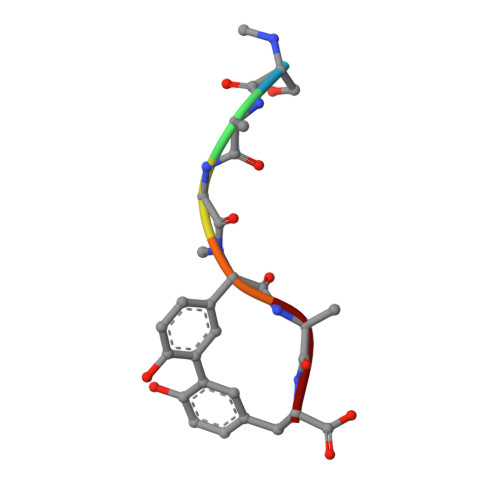
Crystallographic and Biophysical Analysis of a Bacterial Signal Peptidase in Complex with a Lipopeptide Based Inhibitor.
Paetzel, M., Goodall, J.J., Kania, M., Dalbey, R.E., Page, M.G.P.(2004) J Biol Chem 279: 30781
- PubMed: 15136583
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M401686200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1T7D - PubMed Abstract:
We report here the crystallographic and biophysical analysis of a soluble, catalytically active fragment of the Escherichia coli type I signal peptidase (SPase Delta2-75) in complex with arylomycin A2. The 2.5-A resolution structure revealed that the inhibitor is positioned with its COOH-terminal carboxylate oxygen (O45) within hydrogen bonding distance of all the functional groups in the catalytic center of the enzyme (Ser90 O-gamma, Lys145 N-zeta, and Ser88 O-gamma) and that it makes beta-sheet type interactions with the beta-strands that line each side of the binding site. Ligand binding studies, calorimetry, fluorescence spectroscopy, and stopped-flow kinetics were also used to analyze the binding mode of this unique non-covalently bound inhibitor. The crystal structure was solved in the space group P4(3)2(1)2. A detailed comparison is made to the previously published acyl-enzyme inhibitor complex structure (space group: P2(1)2(1)2) and the apo-enzyme structure (space group: P4(1)2(1)2). Together this work provides insights into the binding of pre-protein substrates to signal peptidase and will prove helpful in the development of novel antibiotics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, British Columbia, V5A 1S6 Canada. mpaetze@sfu.ca