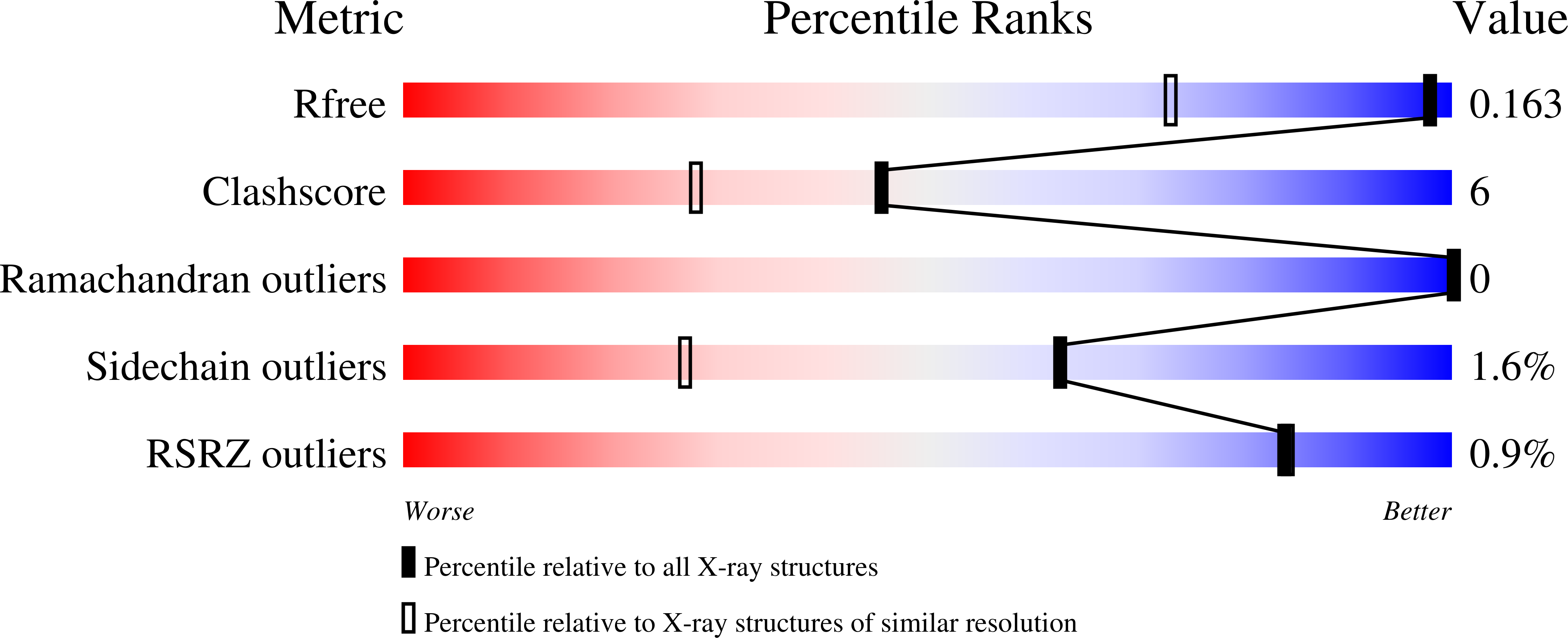
The Humicola Grisea Cel12A Enzyme Structure at 1.2 A Resolution and the Impact of its Free Cysteine Residues on Thermal Stability
Sandgren, M., Gualfetti, P.J., Paech, C., Paech, S., Shaw, A., Gross, L.S., Saldajeno, M., Berglund, G.I., Jones, T.A., Mitchinson, C.(2003) Protein Sci 12: 2782
- PubMed: 14627738
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.03220403
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OLQ, 1OLR - PubMed Abstract:
As part of a program to discover improved glycoside hydrolase family 12 (GH 12) endoglucanases, we have extended our previous work on the structural and biochemical diversity of GH 12 homologs to include the most stable fungal GH 12 found, Humicola grisea Cel12A. The H. grisea enzyme was much more stable to irreversible thermal denaturation than the Trichoderma reesei enzyme. It had an apparent denaturation midpoint (T(m)) of 68.7 degrees C, 14.3 degrees C higher than the T. reesei enzyme. There are an additional three cysteines found in the H. grisea Cel12A enzyme. To determine their importance for thermal stability, we constructed three H. grisea Cel12A single mutants in which these cysteines were exchanged with the corresponding residues in the T. reesei enzyme. We also introduced these cysteine residues into the T. reesei enzyme. The thermal stability of these variants was determined. Substitutions at any of the three positions affected stability, with the largest effect seen in H. grisea C206P, which has a T(m) 9.1 degrees C lower than that of the wild type. The T. reesei cysteine variant that gave the largest increase in stability, with a T(m) 3.9 degrees C higher than wild type, was the P201C mutation, the converse of the destabilizing C206P mutation in H. grisea. To help rationalize the results, we have determined the crystal structure of the H. grisea enzyme and of the most stable T. reesei cysteine variant, P201C. The three cysteines in H. grisea Cel12A play an important role in the thermal stability of this protein, although they are not involved in a disulfide bond.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Uppsala University, Biomedical Center, S-751 24 Uppsala, Sweden.