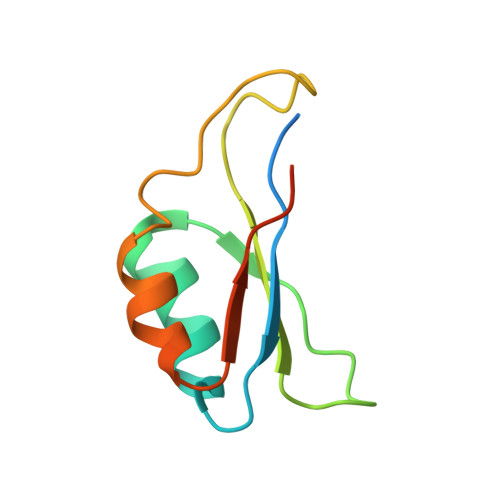
Solution structure of the pro-hormone convertase 1 pro-domain from Mus musculus.
Tangrea, M.A., Bryan, P.N., Sari, N., Orban, J.(2002) J Mol Biol 320: 801-812
- PubMed: 12095256
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)00543-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KN6 - PubMed Abstract:
The solution structure of the mouse pro-hormone convertase (PC) 1 pro-domain was determined using heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy and is the first structure to be obtained for any of the domains in the convertase family. The ensemble of NMR-derived structures shows a well-ordered core consisting of a four-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet with two alpha-helices packed against one side of this sheet. Sequence homology suggests that the other eukaryotic PC pro-domains will have the same overall fold and most of the residues forming the hydrophobic core of PC1 are highly conserved within the PC family. However, some of the core residues are predicted by homology to be replaced by polar amino acid residues in other PC pro-domains and this may help to explain their marginal stability. Interestingly, the folding topology observed here is also seen for the pro-domain of bacterial subtilisin despite little or no sequence homology. Both the prokaryotic and eukaryotic structures have hydrophobic residues clustered on the solvent-accessible surface of their beta-sheets although the individual residue types differ. In the bacterial case this region is buried at the binding interface with the catalytic domain and, in the eukaryotic PC family, these surface residues are conserved. We therefore propose that the hydrophobic patch in the PC1 pro-domain is involved in the binding interface with its cognate catalytic domain in a similar manner to that seen for the bacterial system. The PC1 pro-domain structure also reveals potential mechanisms for the acid-induced dissociation of the complex between pro- and catalytic domains.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Advanced Research in Biotechnology, University of Maryland Biotechnology Institute, 9600 Gudelsky Drive, Rockville, MD 20850, USA.