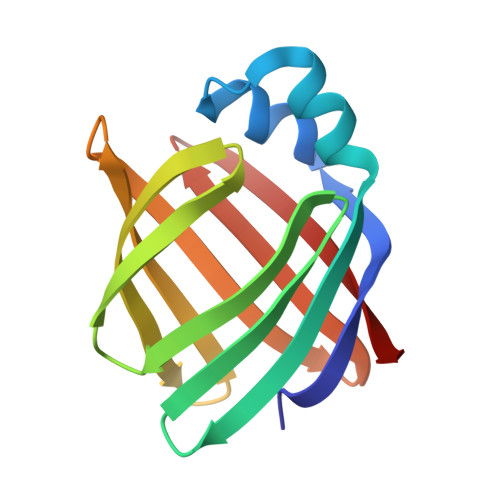
Refined apoprotein structure of rat intestinal fatty acid binding protein produced in Escherichia coli.
Sacchettini, J.C., Gordon, J.I., Banaszak, L.J.(1989) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86: 7736-7740
- PubMed: 2682622
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.86.20.7736
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1IFB - PubMed Abstract:
Rat intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP) is a member of a family of cytoplasmic hydrophobic ligand-binding proteins. To gain insights about the contribution of bound fatty acid to I-FABP's conformation and mechanism of ligand binding, we have determined the structure of Escherichia coli-derived rat apo-I-FABP to 1.96-A resolution and compared it to the recently refined structure of I-FABP with bound palmitate. Both apo- and holo-I-FABP are composed primarily of anti-parallel beta-strands which form two nearly orthogonal beta-sheets ("beta-clam"). The overall structures of the apo- and holo-I-FABP are nearly identical, with a root mean square (rms) difference of 0.37 A between C alpha atoms, 0.38 A between all main-chain atoms, and 0.94 A between all side-chain atoms. However, rms differences of greater than 1.3 A were noted for the side chains of Ile-23, Lys-27, Arg-56, Leu-72, Ala-73, and Asp-74. The space occupied by bound ligand in the core of the holoprotein is occupied in the apo-protein by ordered solvent molecules. This results in an increase in the total number of internal ordered solvent molecules from 7 in the holoprotein to 13 in apo-I-FABP. This finding, together with observed differences in the side-chain orientations of two residues (Arg-56 and Lys-27) situated over a potential opening to the cores of the apo- and holoproteins, suggests that solvent molecules play a critical role in ligand binding. Moreover, the data indicate that the beta-clam structure is stable even in the absence of bound ligand.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Washington University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, MO 63110.