Homologous Proteins with Different Folds: The Three-Dimensional Structures of Domains 1 and 6 of the Multiple Kazal-Type Inhibitor Lekti
Lauber, T., Schulz, A., Schweimer, K., Adermann, K., Marx, U.C.(2003) J Mol Biol 328: 205
- PubMed: 12684009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00245-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1H0Z, 1HDL - PubMed Abstract:
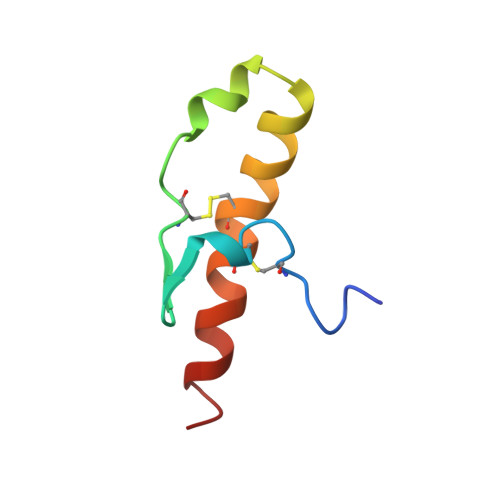
We have determined the solution structures of recombinant domain 1 and native domain 6 of the multi-domain Kazal-type serine proteinase inhibitor LEKTI using multi-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. While two of the 15 potential inhibitory LEKTI domains contain three disulfide bonds typical of Kazal-type inhibitors, the remaining 13 domains have only two of these disulfide bridges. Therefore, they may represent a novel type of serine proteinase inhibitor. The first and the sixth LEKTI domain, which have been isolated from human blood ultrafiltrate, belong to this group. In spite of sharing the same disulfide pattern and a sequence identity of about 35% from the first to the fourth cysteine, the two proteins show different structures in this region. The three-dimensional structure of domain 6 consists of two helices and a beta-hairpin structure, and closely resembles the three-dimensional fold of classical Kazal-type serine proteinase inhibitors including the inhibitory binding loop. Domain 6 has been shown to be an efficient, but non-permanent serine proteinase inhibitor. The backbone geometry of its canonical loop is not as well defined as the remaining structural elements, providing a possible explanation for its non-permanent inhibitory activity. We conclude that domain 6 belongs to a subfamily of classical Kazal-type inhibitors, as the third disulfide bond and a third beta-strand are missing. The three-dimensional structure of domain 1 shows three helices and a beta-hairpin, but the central part of the structure differs remarkably from that of domain 6. The sequence adopting hairpin structure in domain 6 exhibits helical conformation in domain 1, and none of the residues within the putative P3 to P3' stretch features backbone angles that resemble those of the canonical loop of known proteinase inhibitors. No proteinase has been found to be inhibited by domain 1. We conclude that domain 1 adopts a new protein fold and is no canonical serine proteinase inhibitor.
Organizational Affiliation:
Lehrstuhl für Biopolymere, Universität Bayreuth, Universitätstrasse 30, D-95440 Bayreuth, Germany.