Conserved Segments 1A and 2B of the Intermediate Filament Dimer: Their Atomic Structures and Role in Filament Assembly.
Strelkov, S., Herrmann, H., Geisler, N., Wedig, T., Zimbelmann, R., Aebi, U., Burkhard, P.(2002) EMBO J 21: 1255
- PubMed: 11889032
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/21.6.1255
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
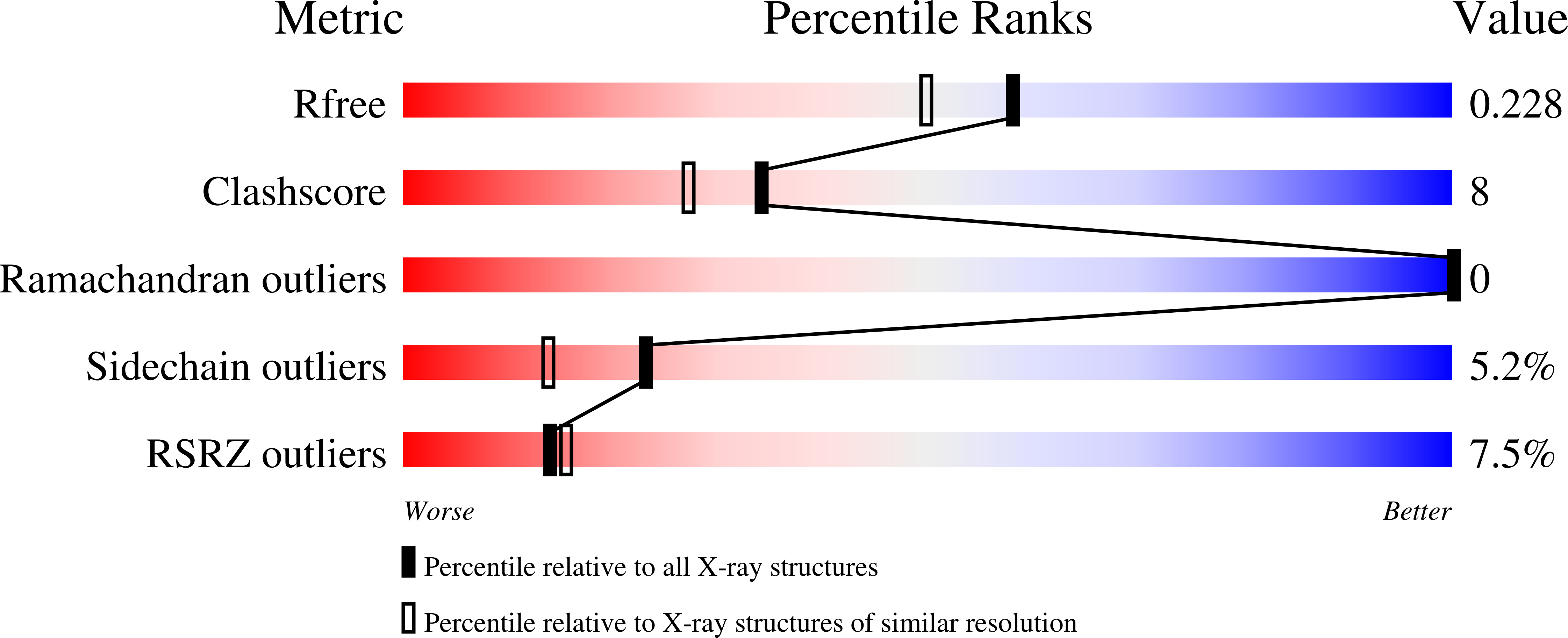
1GK4, 1GK6, 1GK7 - PubMed Abstract:
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are key components of the cytoskeleton in higher eukaryotic cells. The elementary IF 'building block' is an elongated coiled-coil dimer consisting of four consecutive alpha-helical segments. The segments 1A and 2B include highly conserved sequences and are critically involved in IF assembly. Based on the crystal structures of three human vimentin fragments at 1.4-2.3 A resolution (PDB entries 1gk4, 1gk6 and 1gk7), we have established the molecular organization of these two segments. The fragment corresponding to segment 1A forms a single, amphipatic alpha-helix, which is compatible with a coiled-coil geometry. While this segment might yield a coiled coil within an isolated dimer, monomeric 1A helices are likely to play a role in specific dimer-dimer interactions during IF assembly. The 2B segment reveals a double-stranded coiled coil, which unwinds near residue Phe351 to accommodate a 'stutter'. A fragment containing the last seven heptads of 2B interferes heavily with IF assembly and also transforms mature vimentin filaments into a new kind of structure. These results provide the first insight into the architecture and functioning of IFs at the atomic level.
Organizational Affiliation:
Maurice E.Müller Institute for Structural Biology, Biozentrum, University of Basel, Klingelbergstrasse 70, CH-4056 Basel, Switzerland. sergei-v.strelkov@unibas.ch