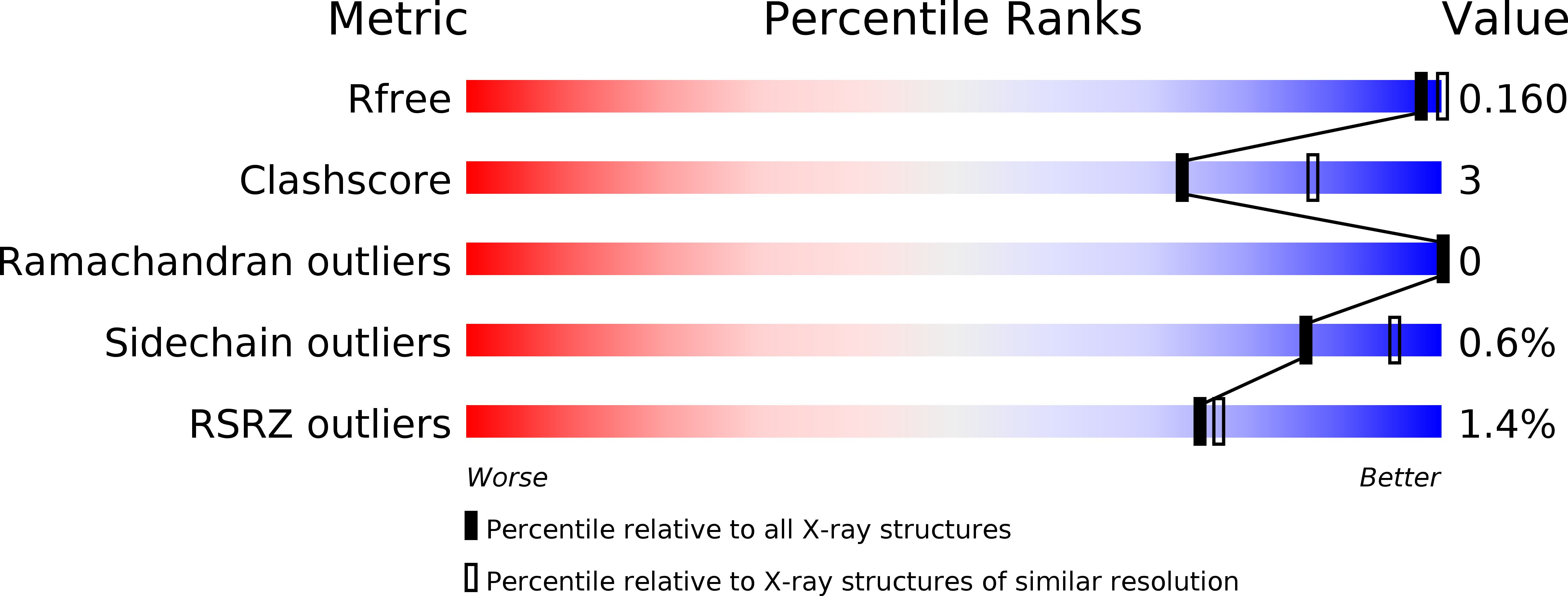
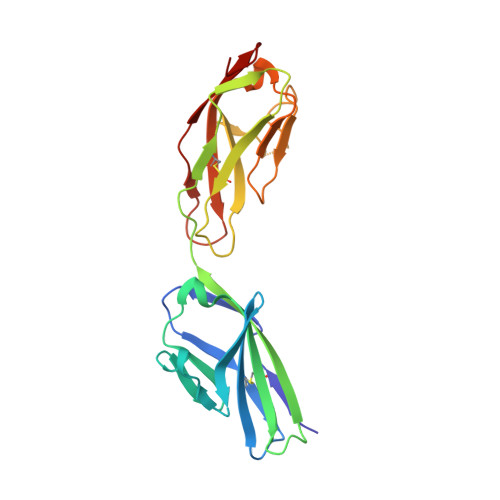X-ray structure of junctional adhesion molecule: structural basis for homophilic adhesion via a novel dimerization motif.
Kostrewa, D., Brockhaus, M., D'Arcy, A., Dale, G.E., Nelboeck, P., Schmid, G., Mueller, F., Bazzoni, G., Dejana, E., Bartfai, T., Winkler, F.K., Hennig, M.(2001) EMBO J 20: 4391-4398
- PubMed: 11500366
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.16.4391
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1F97 - PubMed Abstract:
Junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs) are a family of immunoglobulin-like single-span transmembrane molecules that are expressed in endothelial cells, epithelial cells, leukocytes and myocardia. JAM has been suggested to contribute to the adhesive function of tight junctions and to regulate leukocyte trans migration. We describe the crystal structure of the recombinant extracellular part of mouse JAM (rsJAM) at 2.5 A resolution. rsJAM consists of two immunoglobulin-like domains that are connected by a conformationally restrained short linker. Two rsJAM molecules form a U-shaped dimer with highly complementary interactions between the N-terminal domains. Two salt bridges are formed in a complementary manner by a novel dimerization motif, R(V,I,L)E, which is essential for the formation of rsJAM dimers in solution and common to the known members of the JAM family. Based on the crystal packing and studies with mutant rsJAM, we propose a model for homophilic adhesion of JAM. In this model, U-shaped JAM dimers are oriented in cis on the cell surface and form a two-dimensional network by trans-interactions of their N-terminal domains with JAM dimers from an opposite cell surface.
Organizational Affiliation:
F.Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Pharmaceutical Research, 4070 Basel, Switzerland.