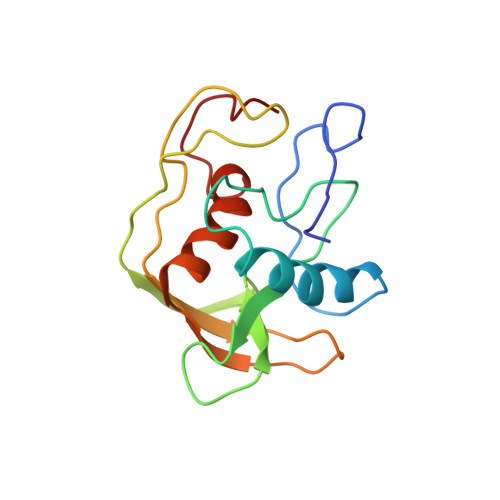
A new subclass of the zinc metalloproteases superfamily revealed by the solution structure of peptide deformylase.
Meinnel, T., Blanquet, S., Dardel, F.(1996) J Mol Biol 262: 375-386
- PubMed: 8845003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1996.0521
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1DEF - PubMed Abstract:
Escherichia coli peptide deformylase, a member of the zinc metalloproteases family, is made up of an active core domain composed of 147 residues and of an additional and dispensable C-terminal tail of 21 residues. The three-dimensional structure of the catalytic core could be studied by NMR. 1H and 15N NMR resonances assignments were obtained by two-dimensional and three-dimensional heteronuclear spectroscopy. The structure could be calculated using a set of 1015 restraints for the 147 residues of the enzyme. The overall structure is composed of a series of antiparallel beta-strands which surround two perpendicular alpha-helices. The C-terminal helix contains the HEXXH motif, which is crucial for activity. This helical arrangement and the way the histidines bind the zinc ion clearly are structurally reminiscent of the other members of the metalloprotease family, such as thermolysin or metzincins. Nevertheless, the overall arrangement of secondary and tertiary structures of peptide deformylase and the positioning of its third zinc ligand (a cysteine) are quite different from those of the other members of the family. These discrepancies, together with several biochemical differences, lead us to propose that peptide deformylase is the first example of a new class of the zinc-metalloproteases family. Studies of the interaction of peptide deformylase with either an inhibitor of the reaction or a product of the catalysed reaction, Met-Ala-Ser, as well as comparisons with the structures of other enzymes of the family, have enabled us to delineate the area corresponding to their binding site. The structural basis of the specificity of recognition of the formyl group is discussed in the context of the protease superfamily.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratoire de Biochimie URA 1970 du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau, France.