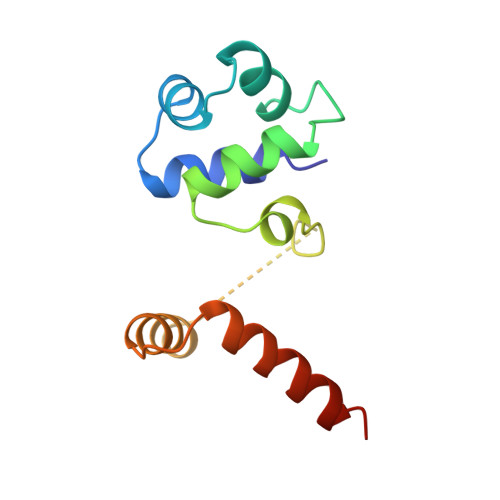
An evolutionary link between sporulation and prophage induction in the structure of a repressor:anti-repressor complex.
Lewis, R.J., Brannigan, J.A., Offen, W.A., Smith, I., Wilkinson, A.J.(1998) J Mol Biol 283: 907-912
- PubMed: 9799632
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1998.2163
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1B0N - PubMed Abstract:
Spore formation is an extreme response of some bacteria to adversity. In Bacillus subtilis the proteins of the sin, sporulation inhibition, region form a component of an elaborate molecular circuitry that regulates the commitment to sporulation. SinR is a tetrameric repressor protein that binds to the promoters of genes essential for entry into sporulation and prevents their transcription. This repression is overcome through the activity of SinI, which disrupts the SinR tetramer through the formation of a SinI-SinR heterodimer. The interactions governing this curious quaternary transition are revealed in the crystal structure of the SinI-SinR complex. The most striking, and unexpected, finding is that the tertiary structure of the DNA-binding domain of SinR is identical with that of the corresponding domains of the repressor proteins, CI and Cro, of bacteriophage 434 that regulate lysis/lysogeny. This structural similarity greatly exceeds that between SinR and any bacterial protein or between the 434 repressor proteins and their homologues in the closely related bacteriophage lambda. The close evolutionary relationship implied by the structures of SinR and the 434 repressors provokes both comparison of their functions and a speculative consideration of the intriguing possibility of an evolutionary link between the two adaptive responses, sporulation and prophage induction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of York, York, YO10 5DD, UK. rick@yorvic.york.ac.uk