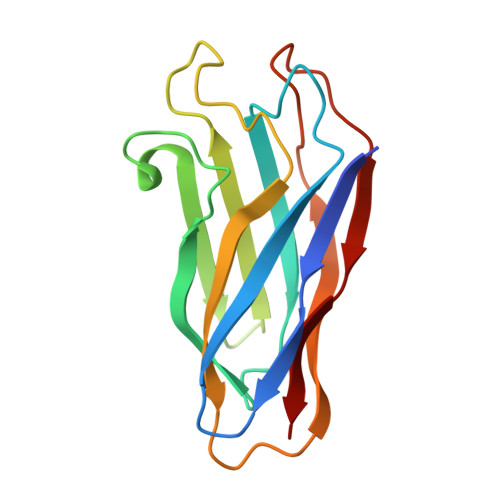
The crystal structure of a type I cohesin domain at 1.7 A resolution.
Tavares, G.A., Beguin, P., Alzari, P.M.(1997) J Mol Biol 273: 701-713
- PubMed: 9402065
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1997.1326
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1AOH - PubMed Abstract:
The quaternary organization of the cellulosome, a multi-enzymatic extracellular complex produced by cellulolytic bacteria, depends on specific interactions between dockerin domains, double EF-hand subunits carried by the catalytic components, and cohesin domains, individual receptor subunits linearly arranged within a non-catalytic scaffolding polypeptide. Cohesin-dockerin complexes with distinct specificities are also thought to mediate the attachment of cellulosomes to the cell membrane. We report here the crystal structure of a single cohesin domain from the scaffolding protein of Clostridium thermocellum. The cohesin domain folds into a nine-stranded beta-sandwich with an overall "jelly roll" topology, similar to that observed in bacterial cellulose-binding domains. Surface-exposed patches of conserved residues promote extensive intermolecular contacts in the crystal, and suggest a possible binding target for the EF-hand pair of the cognate dockerin domain. Comparative studies of cohesin domains indicate that, in spite of low sequence similarities and different functional roles, all cohesin domains share a common nine-stranded beta-barrel fold stabilized by a conserved hydrophobic core. The formation of stable cohesin-dockerin complexes requires the presence of Ca2+. However, the structure of the cohesin domain reported here reveals no obvious Ca2+-binding site, and previous experiments have failed to detect high affinity binding of Ca2+ to the unliganded dockerin domain of endoglucanase CelD. Based on structural and biochemical evidence, we propose a model of the cohesin-dockerin complex in which the dockerin domain requires complexation with its cohesin partner for protein stability and high-affinity Ca2+ binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
Unité d'Immunologie Structurale (URA 1961 CNRS), Paris, France.