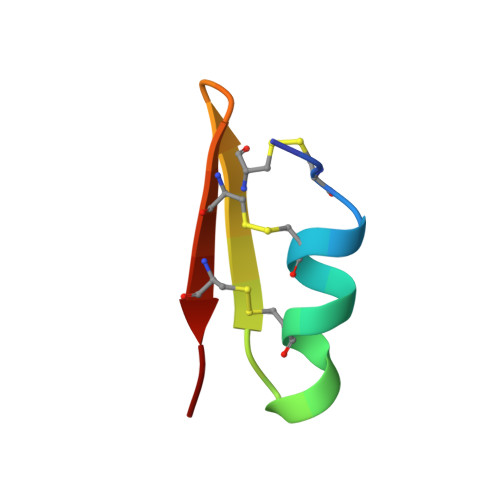
Solution structure of P01, a natural scorpion peptide structurally analogous to scorpion toxins specific for apamin-sensitive potassium channel.
Blanc, E., Fremont, V., Sizun, P., Meunier, S., Van Rietschoten, J., Thevand, A., Bernassau, J.M., Darbon, H.(1996) Proteins 24: 359-369
- PubMed: 8778783
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(199603)24:3<359::AID-PROT9>3.0.CO;2-B
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ACW - PubMed Abstract:
The venom of the North African scorpion Androctonus mauretanicus mauretanicus possesses numerous highly active neurotoxins that specifically bind to various ion channels. One of these, P05, has been found to bind specifically to calcium-activated potassium channels and also to compete with apamin, a toxin extracted from bee venom. Besides the highly potent ones, several of these peptides (including that of P01) have been purified and been found to possess only a very weak, although significant, activity in competition with apamin. The amino acid sequence of P01 shows that it is shorter than P05 by two residues. This deletion occurs within an alpha-helix stretch (residues 5-12). This alpha-helix has been shown to be involved in the interaction of P05 with its receptor via two arginine residues. These two arginines are absent in the P01 sequence. Furthermore, a proline residue in position 7 of the P01 sequence may act as an alpha-helix breaker. We have determined the solution structure of P01 by conventional two-dimensional 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and show that 1) the proline residue does not disturb the alpha-helix running from residues 5 to 12; 2) the two arginines are topologically replaced by two acidic residues, which explains the drop in activity; 3) the residual binding activity may be due to the histidine residue in position 9; and 4) the overall secondary structure is conserved, i.e., an alpha-helix running from residues 5 to 12, two antiparallel stretches of beta-sheet (residues 15-20 and 23-27) connected by a type I' beta-turn, and three disulfide bridges connecting the alpha-helix to the beta-sheet.
Organizational Affiliation:
LCCMB, URA 1296, CNRS IFRC1, Marseille, France.