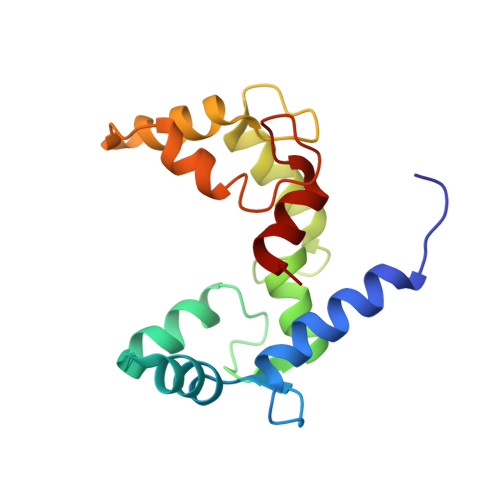
Structural Basis for Simultaneous Binding of Two Carboxy-terminal Peptides of Plant Glutamate Decarboxylase to Calmodulin
Yap, K.L., Yuan, T., Mal, T.K., Vogel, H.J., Ikura, M.(2003) J Mol Biol 328: 193-204
- PubMed: 12684008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00271-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NWD - PubMed Abstract:
Activation of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) by calcium-bound calmodulin (CaM) is required for normal plant growth through regulation of gamma-aminobutyrate and glutamate metabolism. The interaction of CaM with the C-terminal domain of GAD is believed to induce dimerization of the enzyme, an event implicated for Ca(2+)-dependent enzyme activation. Here, we present the solution structure of CaM in complex with a dimer of peptides derived from the C-terminus of Petunia hybrida GAD. The 23 kDa ternary complex is pseudo-symmetrical with each domain of CaM bound to one of the two antiparallel GAD peptides, which form an X-shape with an interhelical angle of 60 degrees. To accommodate the dimeric helical GAD target, the two domains of CaM adopt an orientation markedly different from that seen in other CaM-target complexes. Although the dimeric GAD domain is much larger than previously studied CaM-binding peptides, the two CaM domains appear closer together and make a number of interdomain contacts not observed in earlier complexes. The present structure of a single CaM molecule interacting with two target peptides provides new evidence for the conformational flexibility of CaM as well as a structural basis for the ability of CaM to activate two enzyme molecules simultaneously.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Molecular and Structural Biology, Ontario Cancer Institute and Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, 610 University Avenue, Toronto, Ontario, M5G 2M9, Canada.