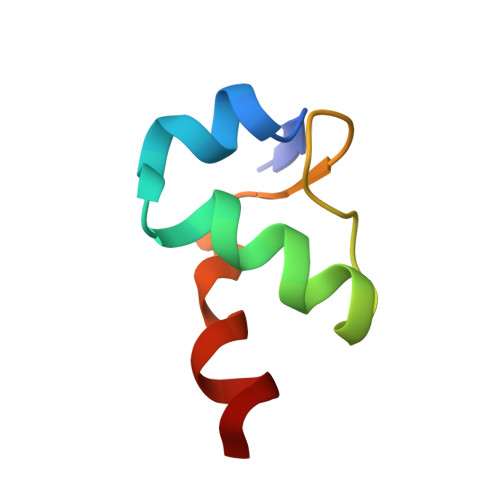
A conserved structural motif at the N terminus of bacterial translation initiation factor IF2
Laursen, B.S., Mortensen, K.K., Sperling-Petersen, H.U., Hoffman, D.W.(2003) J Biol Chem 278: 16320-16328
- PubMed: 12600987
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M212960200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ND9 - PubMed Abstract:
The 18-kDa Domain I from the N-terminal region of translation initiation factor IF2 from Escherichia coli was expressed, purified, and structurally characterized using multidimensional NMR methods. Residues 2-50 were found to form a compact subdomain containing three short beta-strands and three alpha-helices, folded to form a betaalphaalphabetabetaalpha motif with the three helices packed on the same side of a small twisted beta-sheet. The hydrophobic amino acids in the core of the subdomain are conserved in a wide range of species, indicating that a similarly structured motif is present at the N terminus of IF2 in many of the bacteria. External to the compact 50-amino acid subdomain, residues 51-97 are less conserved and do not appear to form a regular structure, whereas residues 98-157 form a helix containing a repetitive sequence of mostly hydrophilic amino acids. Nitrogen-15 relaxation rate measurements provide evidence that the first 50 residues form a well ordered subdomain, whereas other regions of Domain I are significantly more mobile. The compact subdomain at the N terminus of IF2 shows structural homology to the tRNA anticodon stem contact fold domains of the methionyl-tRNA and glutaminyl-tRNA synthetases, and a similar fold is also found in the B5 domain of the phenylalanine-tRNA synthetase. The results of the present work will provide guidance for the design of future experiments directed toward understanding the functional roles of this widely conserved structural domain within IF2.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, University of Aarhus, DK-8000 Aarhus, Denmark.