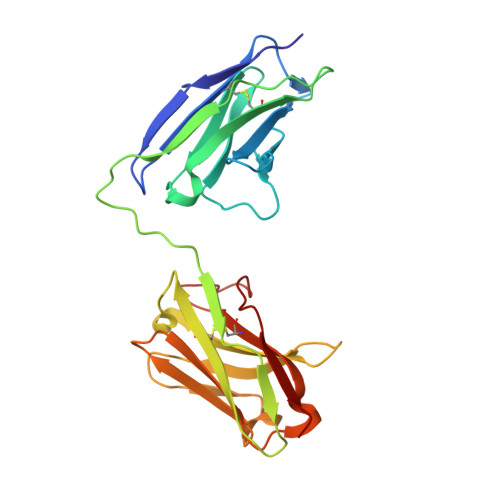
The Crystal Structure of an Anti-CEA scFv Diabody Assembled from T84.66 scFvs in VL-to-VH Orientation: Implications for Diabody Flexibility
Carmichael, J.A., Power, B.E., Garrett, T.P., Yazaki, P.J., Shively, J.E., Raubischek, A.A., Wu, A.M., Hudson, P.J.(2003) J Mol Biol 326: 341-351
- PubMed: 12559905
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01428-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MOE - PubMed Abstract:
Diabodies (scFv dimers) are small, bivalent antibody mimetics of approximately 55kDa in size that possess rapid in vivo targeting pharmacokinetics compared to the intact parent antibody, and may prove highly suitable for imaging and therapeutic applications. Here, we describe T84.66Di, the first diabody crystal structure in which the scFvs comprise V domains linked in the V(L)-to-V(H) orientation. The structure was determined by X-ray diffraction analysis to 2.6 A resolution. The T84.66Di scFv was constructed from the anti-carcinoembryonic antigen (anti-CEA) antibody T84.66 variable domains connected by an eight residue peptide linker to provide flexibility between Fv modules and promote dimer formation with bivalent affinity to the cell-surface target, CEA. Therefore, it was surprising to observe a close association of some Fv module complementarity-determining regions in the T84.66 diabody crystal, especially compared to other diabody structures all of which are linked in the opposite V(H)-to-V(L) orientation. The differences between the arrangement of Fv modules in the T84.66Di V(L)-to-V(H) linked diabody structure compared to the crystal structure of L5MK16 and other proposed V(H)-to-V(L) linked diabodies has been investigated and their potential for flexibility discussed. The comparison between V(H)-to-V(L) and V(L)-to-V(H) linked diabodies revealed in this study represents a limited repertoire of possible diabody Fv orientations, but one that reveals the potential flexibility of these molecules. This analysis therefore provides some signposts that may impact on future molecular designs for these therapeutic molecules with respect to diabody flexibility and avidity.
Organizational Affiliation:
CSIRO Health Sciences and Nutrition, 343 Royal Parade, Parkville 3052, Vic., Australia.