Crystal structure of the global regulator FlhD from Escherichia coli at 1.8 A resolution.
Campos, A., Zhang, R.G., Alkire, R.W., Matsumura, P., Westbrook, E.M.(2001) Mol Microbiol 39: 567-580
- PubMed: 11169099
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02247.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1G8E - PubMed Abstract:
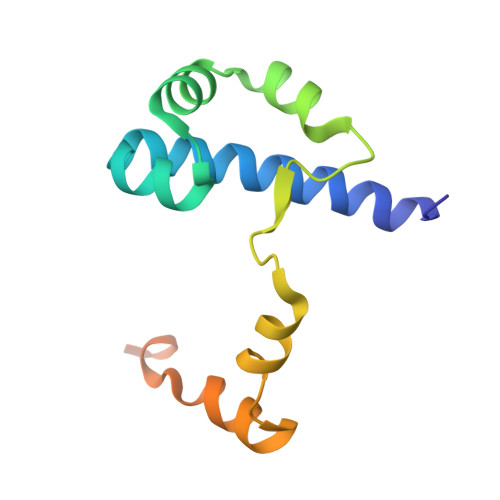
FlhD is a 13.3 kDa transcriptional activator protein of flagellar genes and a global regulator. FlhD activates the transcription of class II operons in the flagellar regulon when complexed with a second protein FlhC (21.5 kDa). FlhD also regulates other expression systems in Escherichia coli. We are seeking to understand this plasticity of FlhD's DNA-binding specificity and, to this end, we have determined the crystal structure of the isolated FlhD protein. The structure was solved by substituting seleno-methionine for natural sulphur-methionine in FlhD, crystallizing the protein and determining the structure factor phases by the method of multiple-energy anomalous dispersion (MAD). The FlhD protein is dimeric. The dimer is tightly coupled, with an intimate contact surface, implying that the dimer does not easily dissociate. The FlhD monomer is predominantly alpha-helical. The C-termini of both FlhD monomers (residues 83-116) are completely disrupted by crystal packing, implying that this region of FlhD is highly flexible. However, part of the C-terminus structure in chain A (residues 83-98) was modelled using a native FlhD crystal. What is seen in chain A suggests a classic DNA-binding, helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif. FlhD does not bind DNA by itself, so it may be that the DNA-binding HTH motif becomes rigidly defined only when FlhD forms a complex with some other protein, such as FlhC. If this were true, it might explain how FlhD exhibits plasticity in its DNA-binding specificity, as each partner protein with which it forms a complex could allosterically affect the binding specificity of its HTH motif. A disulphide bridge is seen between the unique cysteine residues (Cys-65) of FlhD native homodimers. Alanine substitution at Cys-65 does not affect FlhD transcription activator activity, suggesting that the disulphide bond is not necessary for either dimer stability or this function of FlhD. Electrostatic potential analysis indicates that dimeric FlhD has a negatively charged surface.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology and Immunology (M/C 790), College of Medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago, 835 S. Wolcott Ave., MSB E-603, Chicago, IL 60612-7344, USA. acampos@uic.edu