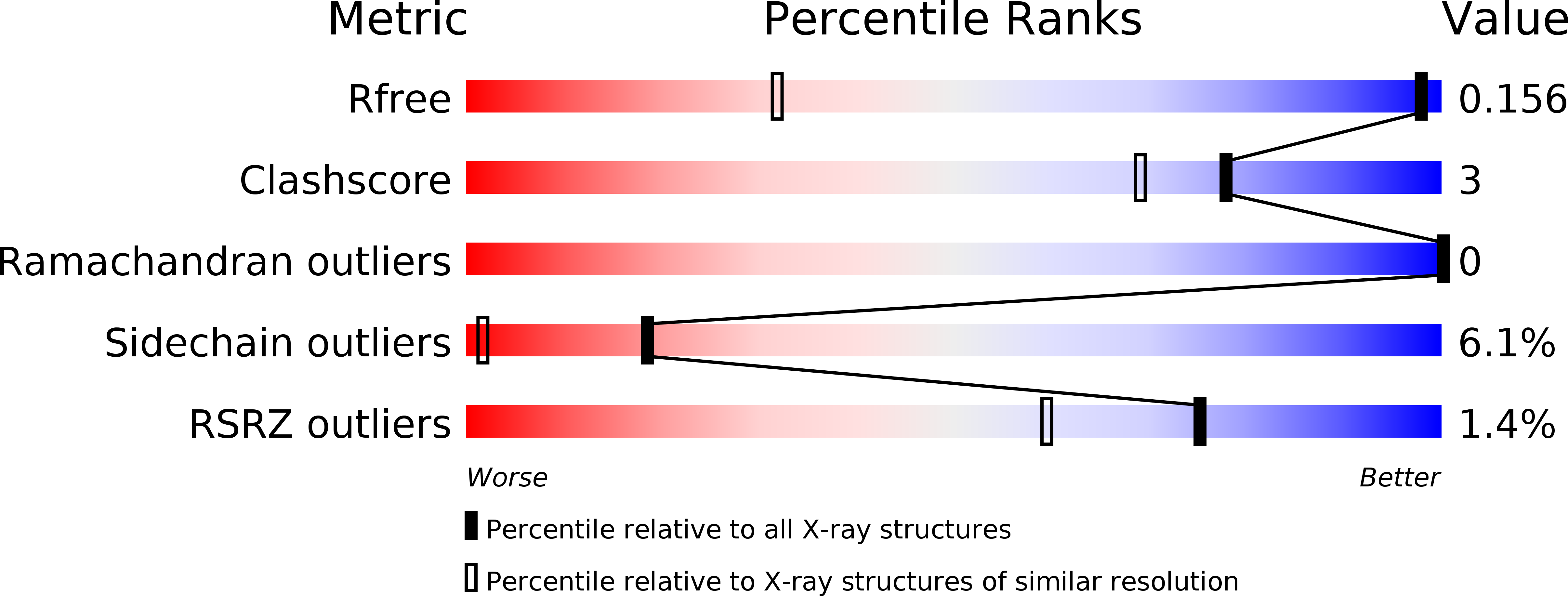
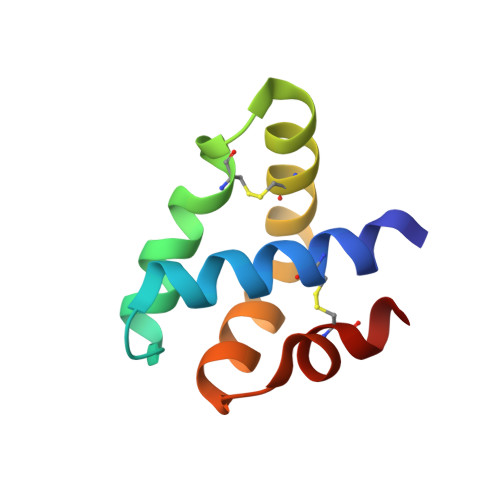
Granulysin Crystal Structure and a Structure-Derived Lytic Mechanism
Anderson, D.H., Sawaya, M.R., Cascio, D., Ernst, W., Modlin, R., Krensky, A., Eisenberg, D.(2002) J Mol Biol 325: 355-365
- PubMed: 12488100
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01234-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1L9L - PubMed Abstract:
Our crystal structure of granulysin suggests a mechanism for lysis of bacterial membranes by granulysin, a 74-residue basic protein from human cytolytic T lymphocyte and natural killer cells. We determined the initial crystal structure of selenomethionyl granulysin by MAD phasing at 2A resolution. We present the structure model refined using native diffraction data to 0.96A resolution. The five-helical bundle of granulysin resembles other "saposin folds" (such as NK-lysin). Positive charges distribute in a ring around the granulysin molecule, and one face has net positive charge. Sulfate ions bind near the segment of the molecule identified as most membrane-lytic and of highest hydrophobic moment. The ion locations may indicate granulysin's orientation of initial approach towards the membrane. The crystal packing reveals one way to pack a sheet of granulysin molecules at the cell surface for a concerted lysis effort. The energy of binding granulysin charges to the bacterial membrane could drive the subsequent lytic processes. The loosely packed core facilitates a hinge or scissors motion towards exposure of hydrophobic surface that we propose tunnels the granulysin into the fracturing target membrane.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute, 5-748 MacDonald, Box 951662, Los Angeles, CA 90095-1662, USA. dha@mbi.ucla.edu